Over 70% of digital platforms fail within their first two years, not due to technical limitations or lack of funding, but because they prioritize technology features over genuine user needs. The most successful digital platform strategies start with a fundamental shift: placing users at the center of every decision rather than leading with impressive technology capabilities.
Building user first digital platforms represents more than just good design practice—it’s a strategic approach that can determine whether your platform thrives or becomes another statistic. Companies that embrace user-first development see 3x higher user engagement rates, 2.5x better retention, and significantly lower customer acquisition costs compared to technology-first approaches. Consistently providing high-quality and relevant content helps attract and retain user attention, further enhancing engagement and retention. A strong brand, built through consistent design elements and a clear brand promise, helps platforms stand out amid information overload and builds user trust.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through every aspect of creating platforms that users genuinely love and actively recommend. From initial user research to technical architecture decisions, we’ll explore how successful digital platform development puts user value at the core of every choice. Knowledge platforms, for instance, focus on organizing and sharing information, making them ideal for universities, nonprofits, or corporations. Businesses of all types, including knowledge-based businesses, benefit from enhanced engagement, interaction, and value delivery through user-first digital platforms.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Makes a Platform Truly User-First
A user-first approach fundamentally inverts traditional platform development by starting with user needs rather than technical capabilities. Instead of asking “What can our technology do?” user-first development begins with “What problems do our users need solved?”
This shift creates platforms designed around actual human behavior rather than assumed requirements. Aligning your platform with user expectations and behaviors is crucial for achieving product market fit and long-term retention. Traditional platform development often struggles because organizations invest heavily in foundational technology first, when these decisions should actually come after thoroughly understanding user needs. Prioritizing user experience involves creating an intuitive interface that simplifies navigation, ensuring users can easily achieve their goals.
Key principles that define user-first platforms include:
Accessibility as a foundation: Every feature must be usable by people with diverse abilities, following WCAG 2.1 standards and inclusive design practices that expand your user base while building trust.
Intuitive navigation patterns: Users should accomplish their goals without extensive training or documentation. Clear information architecture guides users naturally through their intended journey.
Value-driven features: Each capability directly addresses identified user pain points rather than showcasing technical sophistication.
Seamless interactions: Friction disappears through thoughtful design that anticipates user needs and removes unnecessary steps. Integrating various tools, APIs, and frameworks is essential for creating a seamless experience for users, ensuring all systems work harmoniously to enhance usability and satisfaction.
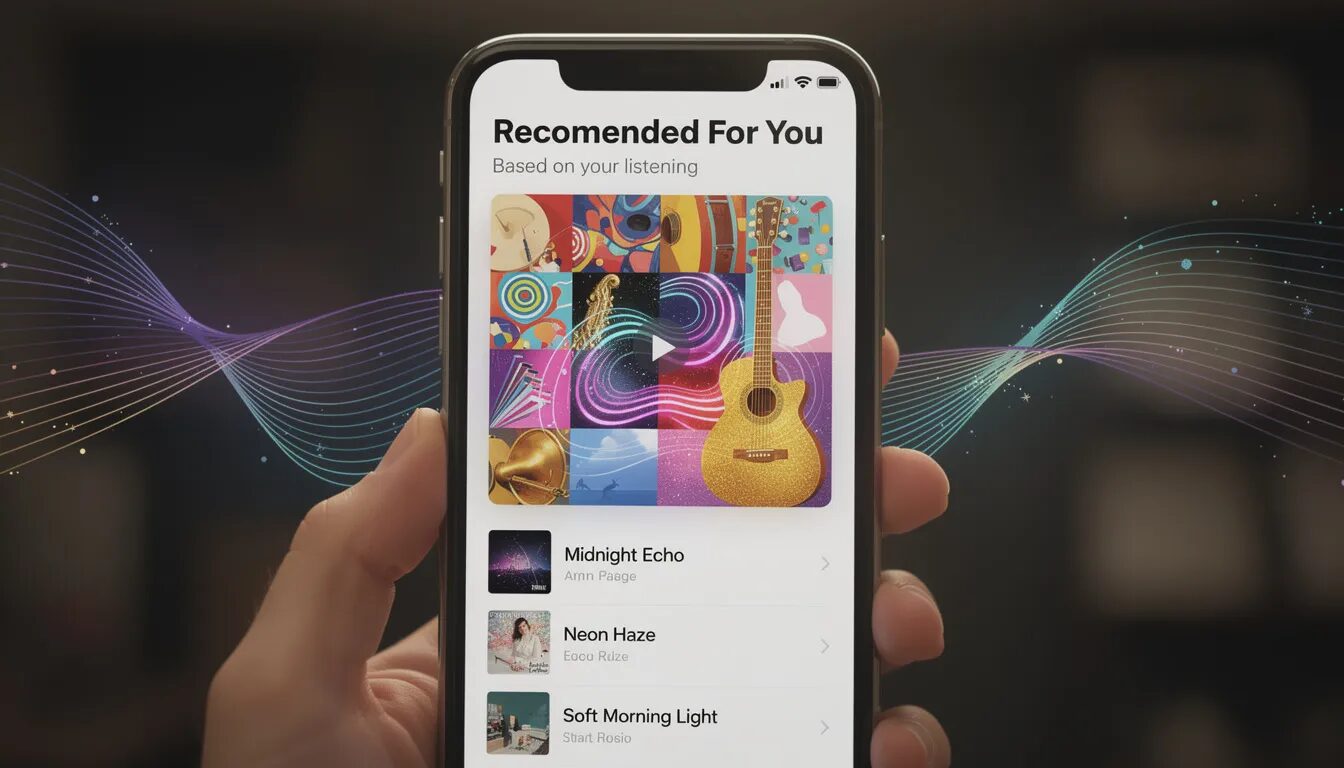
Consider Spotify’s personalized recommendations system. Rather than overwhelming users with every possible music discovery feature, Spotify focuses on understanding individual listening patterns and delivering highly relevant suggestions. This user-first approach has driven massive user engagement because the platform genuinely understands and serves user preferences.
Similarly, Airbnb built trust-building features like verified profiles, secure messaging, and transparent reviews because they recognized that user concerns about safety and authenticity were primary barriers to platform adoption. These features directly addressed real user anxieties rather than adding complexity for its own sake.
The shift from feature-heavy platforms to purpose-driven, user-centric solutions directly impacts platform adoption rates and long-term success. Platforms designed with user-first principles see adoption rates 4x higher than technology-first alternatives because users immediately understand the value proposition and can easily accomplish their goals.
Understanding Your Users Before Building
Successful digital platform development begins with comprehensive user understanding that goes far deeper than basic demographics. The most effective platforms emerge from rigorous research that reveals user motivations, frustrations, and desired outcomes rather than assumed requirements.
Sharing insights gained from this user research can help establish thought leadership, positioning your platform as an industry authority.
Comprehensive User Research Methodologies
User interviews and surveys: Conduct in-depth conversations with 15-20 potential users from each target segment. Focus on understanding their current solutions, pain points, and ideal outcomes rather than asking about specific features.
Behavioral analytics review: Analyze how users currently solve problems your platform aims to address. Study existing tools, workarounds, and the steps people take to accomplish their goals.
Persona development: Create detailed user personas that capture behavioral patterns, motivations, and context rather than just demographic information. Include their technical comfort level, time constraints, and decision-making factors.
Competitive analysis focused on user experience: Examine competitor platforms through the user’s lens. Identify experience gaps, friction points, and opportunities to deliver superior user value. Monitoring competition provides insights that can help differentiate a digital platform in the market, ensuring it stands out and meets user expectations.
Creating Detailed User Journey Maps
Map every touchpoint from initial awareness through ongoing platform use. Identify specific moments where users experience friction, confusion, or delight. These “critical moments” become the foundation for your entire platform strategy.
Understanding user motivations requires uncovering why people need your platform solution. Are they seeking efficiency, connection, learning, or something else entirely? The most successful platform vision emerges from deep understanding of these underlying drivers.
User feedback loops must be established before development begins. Create channels for ongoing input through surveys, user testing sessions, and direct communication. Users should feel heard throughout the platform journey, not just during initial research phases.
Real-world case studies demonstrate the power of thorough user research. When Slack was developing their platform, they spent months understanding how teams actually communicate and collaborate. This research revealed that most business communication tools failed because they didn’t match natural conversation patterns. Slack’s user-first approach led to features like threaded conversations and emoji reactions that felt intuitive because they matched real human communication behaviors.
Core Principles of User-Centric Platform Design
User-centric design principles form the foundation of every successful digital platform. These principles ensure that every design decision serves user needs while maintaining business viability and technical feasibility.
Platforms like app builders or community hubs often use modular and scalable solutions to facilitate growth and the addition of new features.
Simplicity Over Complexity: The 80/20 Rule
Focus your core features on solving the 80% of user needs that occur most frequently. Advanced functionality should enhance rather than complicate the primary user experience. Users should accomplish their main goals within 3-4 clicks from any starting point on your platform.
Accessibility Standards Compliance and Inclusive Design
WCAG 2.1 compliance isn’t just about legal requirements—it’s about expanding your potential user base and demonstrating commitment to all users. Inclusive design practices ensure your platform works across different:
- Physical and cognitive abilities
- Technical skill levels
- Device capabilities and screen sizes
- Internet connection speeds
- Cultural and linguistic backgrounds
It’s also important to adapt existing ones—such as features or systems—to improve accessibility and inclusiveness for all users.
Maintain a uniform look and feel across all platforms to build trust and make the interface more intuitive.
Mobile-First Responsive Design
With over 60% of platform access happening on mobile devices, mobile-first design has become essential. This means designing the mobile experience first, then enhancing for larger screen sizes rather than shrinking desktop designs to fit smaller screens.
Your platform must provide equivalent functionality across different screen sizes while optimizing interactions for touch interfaces. Consider how users behave differently on mobile devices—shorter sessions, thumb navigation, and context switching between other platforms.
Clear Information Architecture and Navigation
Users should never wonder where they are or how to reach their destination. Information architecture should reflect user mental models rather than internal organizational structure. Navigation patterns should remain consistent across all platform areas.
Implement breadcrumbs, clear page titles, and logical groupings that help users maintain orientation. Search functionality should support both specific queries and exploratory discovery.
Consistent UI/UX Patterns
Reusable components and interaction patterns reduce cognitive load and improve user confidence. When users learn how one part of your platform works, that knowledge should transfer to other areas seamlessly.
Maintain consistent:
- Button styles and behaviors
- Form layouts and validation messages
- Loading states and error handling
- Typography and color usage
Performance Optimization for User Experience
Fast loading times directly impact user satisfaction and platform adoption. Users expect pages to load within 2-3 seconds, and even small delays increase drop off points significantly. Optimize performance by treating site speed as a design constraint and using techniques like image optimization to ensure a seamless user experience. Integrating prescriptive design methodologies with artificial intelligence can act as a powerful engine for rapid innovation and systematic technological advancement, further enhancing performance optimization.
Optimize for performance through:
- Image compression and lazy loading
- Code splitting and caching strategies
- Content delivery networks for global users
- Progressive loading of non-critical elements
Designing for Different User Types
Understanding that different users have different needs and skill levels allows you to create more targeted and effective experiences.
Power Users vs Casual Users
Power users need advanced functionality, keyboard shortcuts, and customization options. They’re willing to learn complex features if those features provide significant value and efficiency gains.
Casual users prioritize simplicity and guidance. They need clear instructions, intuitive interfaces, and forgiving error handling. Most value comes from accomplishing basic tasks quickly and confidently.
Design your platform to serve both groups without forcing either to compromise. Implement progressive disclosure that reveals advanced features as users develop expertise while keeping core functionality accessible to newcomers.
Multi-Sided Platforms: Balancing Different Stakeholders
Marketplace and two-sided platforms must optimize experiences for buyers, sellers, and potentially other stakeholders like service providers or administrators. Each group has different goals, success metrics, and workflow requirements.
Create distinct user flows for each stakeholder while maintaining a cohesive overall experience. Ensure that improvements for one group don’t negatively impact others, and look for features that benefit multiple stakeholders simultaneously. Flexibility in a digital platform allows organizations to innovate faster and adapt to market feedback with greater efficiency, ensuring long-term success.
B2B vs B2C User Experience Considerations
B2B platforms require features like team collaboration, admin controls, detailed reporting, and integration with existing business systems. Users often need to justify purchases to others and require clear ROI demonstration.
B2C platforms focus more on individual satisfaction, ease of use, and emotional engagement. Decision-making is typically faster, but competition for attention is higher.
Age Demographics and Digital Literacy
Different age groups bring different expectations and comfort levels with technology. Design should accommodate varying levels of digital literacy without appearing condescending or overly simplified.
Consider implementing optional tutorials, contextual help, and multiple ways to accomplish the same task to serve users with different comfort levels and learning preferences.
Building Your User-First Platform Strategy
An effective digital platform strategy begins with user problems rather than technical capabilities. This approach ensures that every strategic decision serves real user needs while building a sustainable business model. A clear platform strategy helps organizations manage both their current operations and future transformation simultaneously, enabling them to remain competitive in a rapidly changing market. Integrating AI and building a well-connected digital platform can significantly enhance customer experience, leading to higher satisfaction and engagement. A well-defined purpose helps in designing features and marketing messages that resonate with users, ensuring alignment with user expectations and needs.
Starting with User Problems Rather Than Technical Capabilities
The most common mistake in platform strategy involves falling in love with impressive technology before validating user demand. Successful platform development reverses this by identifying specific user problems, validating the importance of solving them, and only then selecting technologies that best serve those needs.
Begin by cataloging the top 5-7 problems your target users face in their current workflows. Prioritize these problems based on frequency, impact, and user willingness to pay for solutions. Your platform vision should directly address these prioritized pain points.
Minimum Viable Product Development for Core User Needs
Your minimum viable product should solve one primary user problem exceptionally well rather than solving multiple problems adequately. This focused approach allows you to validate your core value proposition and gather meaningful user feedback before expanding functionality.
The most effective MVP development follows a clear sequence: 1. Identify the single most critical user problem 2. Design the simplest possible solution that provides real value 3. Build core features that directly address this problem 4. Test with real users and measure problem-solving effectiveness 5. Iterate based on user feedback before adding new capabilities. Prioritize features by focusing on a clear vision and using an agile development approach with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP).
- Identify the single most critical user problem
- Design the simplest possible solution that provides real value
- Build core features that directly address this problem
- Test with real users and measure problem-solving effectiveness
- Iterate based on user feedback before adding new capabilities
Iterative Development Cycles with User Testing
Implement 2-week development cycles that include user testing and feedback integration. Each cycle should deliver measurable improvements in user satisfaction or task completion rates.
Continuous improvements emerge from systematic user feedback rather than internal assumptions about what users want. Establish regular touchpoints with users through surveys, usage analytics, and direct communication channels.
Feature Prioritization Based on User Value
Prioritize features using a framework that weighs user impact against development effort. Features that solve high-impact user problems with relatively low development complexity should take priority over impressive but complex capabilities that serve edge cases.
Consider user feedback, usage analytics, and strategic business objectives when making feature decisions. Maintain a clear product roadmap that users can understand and anticipate.
User-Centric Success Metrics
Traditional business KPIs like revenue and user acquisition remain important, but user-first platforms require additional metrics that measure user satisfaction and value delivery:
- Task completion rates for core user workflows
- Time to value (how quickly new users achieve their first success)
- User engagement depth beyond simple page views
- User-generated feedback sentiment and satisfaction scores
- Feature adoption rates and usage patterns

An effective iterative process means treating each development cycle as a learning opportunity. User behavior data should inform each subsequent iteration, creating a feedback loop that continuously improves user satisfaction while building business value.
Technical Architecture for User Experience
The technology infrastructure supporting your platform must prioritize user experience while maintaining performance, security, and scalability. Technical decisions should enhance rather than constrain user-focused capabilities. A successful digital platform connects seamlessly with other platforms, partners, suppliers, or external services, ensuring a cohesive ecosystem that supports user needs and business objectives. Legacy e-commerce systems often present significant integration challenges, making it crucial to adopt a robust platform strategy for scaling and modernizing e-commerce operations.
API-First Development for Flexible User-Focused Integrations
API-first architecture enables your platform to integrate seamlessly with other tools and platforms your users already use. This approach reduces friction by allowing users to maintain their existing workflows while adding your platform’s value. A robust platform supports core business capabilities by offering widely available Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), enabling seamless integration of internal and external applications. Well-integrated and extensive APIs are important for a smooth and future-proof platform, ensuring that your platform remains adaptable to evolving user needs and technological advancements.
Design APIs that support the user actions and data flows that matter most to your audience. Prioritize integrations with existing systems that users rely on daily, such as CRM, productivity tools, or communication platforms.
Scalable Cloud Based Infrastructure for Performance
Cloud based infrastructure provides the flexibility to maintain consistent user experience as your user base grows. Choose solutions that can automatically scale during peak usage periods without degrading performance. Flexibility in a digital platform supports core business capabilities by offering widely available Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). A robust digital platform provides a foundation for structuring the technological backbone of a business, creating significant opportunities for growth and innovation.
Consider global user distribution when selecting cloud providers and infrastructure design. Users in different geographic regions should experience similar performance levels regardless of physical distance from your servers.
Security and Privacy by Design for User Trust
User trust depends on demonstrating clear commitment to data protection and privacy. Implement security measures that protect user information while maintaining transparent communication about data usage. Digital platforms often contain a lot of sensitive data, necessitating the implementation of compliance measures and security protocols to safeguard user information effectively.
Privacy-by-design principles should influence every technical decision from data collection to storage to processing. Users should understand exactly what data you collect, how it’s used, and how they can control their information.
Real Time Interactions for Immediate User Feedback
Modern users expect immediate responses to their actions. Implement real-time capabilities that provide instant feedback for user interactions, whether through immediate visual responses or live data updates.
Real time interactions become particularly important for collaborative platforms where multiple users need to see each other’s actions immediately, or for platforms where users make time-sensitive decisions.
Progressive Web App Technologies
PWA technologies provide app-like experiences through web browsers, reducing barriers to platform adoption while providing native app capabilities like offline access and push notifications.
Progressive web apps eliminate the friction of app store downloads while providing better user experiences than traditional web applications. Users can access your platform immediately while still receiving app-like functionality.
Content Delivery Networks for Global Performance
CDN implementation ensures that users worldwide experience consistent loading times and performance. This becomes critical for platforms serving global audiences or handling media-heavy content.
Data and Analytics for User Insights
Data collection and analysis must serve user experience improvement rather than just tracking business metrics. Focus on gathering insights that directly inform user experience enhancements. Data-driven decision-making helps in identifying areas for improvement and prioritizing new features, ensuring that platform updates align with user needs.
User Behavior Tracking Tools
Implement analytics tools that reveal how users actually interact with your platform rather than just measuring page views or session duration:
- Google Analytics 4: Provides event-based tracking that reveals user paths and conversion patterns
- Mixpanel: Focuses on user actions and behaviors rather than page-based metrics
- Amplitude: Offers advanced cohort analysis and user journey visualization
A/B Testing Frameworks for Data-Driven UX Improvements
Systematic A/B testing allows you to make user experience improvements based on actual user behavior rather than assumptions. Test one change at a time to isolate the impact of specific modifications.
Focus testing on elements that directly affect user success rates, task completion, and satisfaction rather than just optimizing for clicks or views.
Privacy-Compliant Data Collection
Implement data collection practices that comply with GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy regulations while still gathering insights needed for user experience improvements. Clear user consent and transparent data usage policies build trust while enabling effective analytics.
Real-Time User Feedback Systems
In-app survey tools and feedback widgets allow users to provide immediate input about their experiences. This qualitative data complements quantitative analytics to provide complete insight into user needs and satisfaction.
Choosing the Right Platform Type for Your Users
Different user needs require different platform approaches. Selecting the right platform type based on user goals and behaviors ensures that your technical architecture supports rather than constrains user success.
Community Platforms for User Engagement and Networking
Community platforms serve users who need to connect users with shared interests, goals, or challenges. Success depends on facilitating meaningful interactions and building user engagement over time.
Design community features that encourage regular participation while providing clear value for both active contributors and passive consumers of content. Consider how to recognize valuable community members and incentivize ongoing participation. Member communities, in particular, focus on exclusive access and value, offering curated content, events, and networking tools for verified members only.
Marketplace Platforms for Seamless Transactions
Marketplace platforms must optimize experiences for both buyers and sellers while facilitating smooth transactions. Focus on building user trust through transparent processes, secure payments, and effective dispute resolution.
Successful marketplaces reduce friction at every step of the buying and selling process while providing sufficient information for confident decision making from all parties.
Knowledge Platforms for Information Discovery
Knowledge platforms serve users seeking to learn, research, or access specific information efficiently. Optimize for search functionality, content organization, and various learning styles.
Consider how users with different expertise levels can both consume and contribute knowledge effectively. Implement features that help users discover relevant information they weren’t specifically searching for.
SaaS Platforms with Intuitive Workflows
Software-as-a-Service platforms must integrate seamlessly into users’ existing workflows while providing significant efficiency or capability improvements. Focus on reducing learning curves and time-to-value for new users.
Successful SaaS platforms become indispensable by solving real workflow problems better than alternative solutions or manual processes.
Matching Platforms with Smart Recommendations
Matching platforms connect users with relevant people, content, or opportunities through algorithmic recommendations. Success depends on understanding user preferences and delivering increasingly accurate suggestions. For example, matchmaking platforms connect two sides of a market, such as startups and investors or mentors and mentees.
Implement machine learning capabilities that improve recommendation accuracy as users interact with your platform and provide feedback on suggestions.
Hybrid Platforms with Multiple Value Propositions
Some user needs are best served by combining multiple platform types. Hybrid platforms can provide comprehensive solutions but risk becoming unfocused or overwhelming.
Maintain clear primary use cases while ensuring that secondary features enhance rather than complicate the core user experience.
User Onboarding and Retention Strategies
The first user experience with your platform often determines long-term success. Effective onboarding demonstrates value quickly while building user confidence in platform capabilities. A well-designed landing page is essential for streamlining onboarding and guiding users to the core features of your platform.
Progressive Onboarding with Clear Value Demonstration
Guide new users through your platform’s core functionality step-by-step, showing concrete value at each stage. Avoid overwhelming users with every available feature during initial sessions.
Progressive onboarding allows users to master basic functionality before introducing advanced capabilities. Each step should provide immediate value while preparing users for more sophisticated use cases.
Personalized Welcome Experiences
Tailor initial experiences based on user type, stated goals, or signup source. Different user segments may need different onboarding paths to reach their first success quickly.
Personalized experiences help users understand how your platform applies specifically to their situation rather than requiring them to extrapolate from generic examples.
Interactive Tutorials and Guided Tours
Provide hands-on learning opportunities that let users practice platform functionality in a controlled environment. Interactive tutorials should use real or realistic data that demonstrates actual value rather than abstract examples.
Guided tours should be skippable for experienced users while remaining available for reference when needed.
Gamification Elements for Continued Engagement
Thoughtful gamification can encourage exploration and ongoing platform use without feeling manipulative. Focus on recognizing user progress toward their actual goals rather than arbitrary platform engagement metrics.
Effective gamification celebrates user achievements and milestones that matter to users personally while encouraging continued platform exploration. Integrating interactive elements like polls and quizzes can motivate users and foster a sense of accomplishment, enhancing engagement and satisfaction.
Email and In-App Messaging for User Activation
Develop communication sequences that provide ongoing value while encouraging deeper platform engagement. Messages should help users discover relevant features and achieve their goals rather than simply promoting platform usage.
Balance communication frequency to provide helpful information without overwhelming users with excessive messaging.
Community Building for User Stickiness
Create opportunities for users to connect with each other around shared interests or goals related to your platform. Community features increase user satisfaction while creating network effects that improve retention.
Strong communities become valuable enough that users remain active on your platform partly to maintain those relationships and connections.

Monetization Models That Prioritize User Value
Successful platform monetization aligns revenue generation with user value delivery. The most sustainable business models ensure that paying customers receive proportional value increases rather than feeling exploited.
Freemium Models with Clear Value Progression
Freemium platforms should provide genuine value in free tiers while creating clear incentives for premium upgrades. Users should understand exactly what additional value they’ll receive by upgrading and why that value justifies the cost.
Avoid artificially limiting free tiers in ways that create frustration rather than motivation to upgrade. Free users should achieve real success before encountering premium limitations.
Subscription Tiers Based on User Needs
Design pricing model tiers around actual user behavior patterns and value requirements rather than arbitrary feature combinations. Different user types should find tiers that match their specific needs and usage patterns.
Consider usage-based pricing that scales with the value users receive rather than imposing rigid limits that don’t reflect actual user needs.
Transaction-Based Revenue That Adds Value
When taking transaction fees, ensure that your platform provides clear value that justifies the cost. Transaction fees should support features like payment processing, fraud protection, dispute resolution, or other services that benefit users.
Transparent fee structures help users understand exactly what they’re paying for and why those services provide value worth the cost.
Advertising Models That Enhance User Experience
Advertising can enhance rather than disrupt user experience when ads provide relevant information or opportunities that align with user interests and goals.
Avoid advertising approaches that interrupt core user workflows or compromise user trust through excessive data collection or irrelevant content.
Partnership and Integration Revenue
Revenue from partnerships with complementary services can provide value to users while generating income for your platform. Focus on partnerships that genuinely expand user capabilities or solve adjacent problems.
Transparent Pricing for User Trust
Clear, honest pricing builds user trust and reduces barriers to purchasing decisions. Avoid hidden fees, confusing terms, or pricing structures that make it difficult for users to understand total costs.
Competitive advantage often comes from pricing transparency and simplicity rather than complex structures that obscure true costs.
Measuring User-First Platform Success
Success metrics for user-first platforms extend beyond traditional business KPIs to include measures of user satisfaction, value delivery, and experience quality.
User Satisfaction Metrics
Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measures user willingness to recommend your platform to others, indicating overall satisfaction and perceived value.
Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Provides direct feedback on user experience quality and identifies areas for improvement.
Regular satisfaction surveys should focus on understanding why users feel satisfied or dissatisfied rather than just capturing numerical scores.
Engagement Metrics That Matter
Daily and monthly active users: Track consistent platform usage that indicates ongoing value delivery rather than one-time interactions.
Session duration and depth: Measure meaningful engagement with core platform features rather than just time spent browsing.
Feature adoption rates: Monitor how users discover and adopt new capabilities, indicating successful feature design and communication.
User Retention and Churn Analysis
Cohort tracking reveals how user engagement changes over time and identifies patterns in user lifecycle management. Understanding why users remain active or become inactive guides improvement priorities.
Analyze churn patterns to identify early warning signs and intervention opportunities that might retain at-risk users.
Support and User Experience Indicators
Support ticket volume and resolution time: Lower ticket volumes often indicate intuitive design, while faster resolution demonstrates commitment to user success.
User-generated content and community health: Active user contributions indicate engagement and platform value beyond core functionality.
Accessibility Compliance and Usability Testing
Regular accessibility audits ensure your platform serves users with diverse abilities while maintaining compliance with legal requirements.
Usability testing with real users reveals friction points and improvement opportunities that analytics alone cannot identify.
Business Impact Metrics
While user satisfaction remains primary, successful platforms also deliver business results:
- User lifetime value and retention rates
- Customer acquisition costs and organic growth
- Revenue per user and pricing model effectiveness
- Market share and competitive positioning
The most successful digital platform organizations track user-centric metrics alongside business metrics, recognizing that long-term business success depends on consistent user value delivery.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Understanding common platform development mistakes helps avoid costly errors that compromise user experience and business success.
Feature Creep: Maintaining Focus on Core User Needs
The temptation to add impressive features can distract from solving core user problems exceptionally well. Feature creep occurs when platforms accumulate capabilities that serve edge cases or showcase technical prowess rather than addressing primary user needs.
Avoid feature creep by maintaining clear criteria for new feature evaluation. Each proposed feature should solve identified user problems and integrate naturally with existing workflows rather than creating additional complexity.
Technology-First Thinking: Avoiding Impressive Tech Over User Value
Emerging technologies can be seductive, but implementing them without clear user value often creates solutions searching for problems. Blockchain, AI, or other sophisticated technologies should serve specific user needs rather than being added for competitive advantage alone.
Evaluate technology decisions based on how they improve user outcomes rather than how they position your platform technically in the market.
Ignoring User Feedback: Systematic Process Integration
Collecting user feedback without systematic integration into development priorities wastes both user time and business opportunities. Create formal processes for reviewing, prioritizing, and responding to user input.
User feedback should influence product roadmaps, feature priorities, and design decisions through structured evaluation rather than ad-hoc implementation.
One-Size-Fits-All Approaches: Recognizing User Diversity
Designing for “average” users often serves no users well. Different user segments have distinct needs, technical comfort levels, and success criteria that require different approaches.
Implement flexibility that allows different user types to customize their experience while maintaining platform coherence and usability.
Poor Mobile Experience: Mobile Users as Primary Citizens
Treating mobile users as afterthoughts creates suboptimal experiences for the majority of users. Mobile-first design ensures that all users receive appropriate experiences regardless of their device choice.
Consider mobile-specific user behaviors, constraints, and interaction patterns rather than simply adapting desktop interfaces for smaller screen sizes.
Neglecting Accessibility: Building Inclusively from the Start
Adding accessibility features after development costs significantly more than building inclusively from the beginning. Accessibility considerations should influence design, development, and testing processes throughout platform creation.
Inclusive design principles benefit all users while expanding market reach and demonstrating social responsibility.
Implementation Roadmap for User-First Platforms
Successful platform development follows a structured timeline that balances user research, iterative development, and continuous improvement.
Phase 1: User Research and Validation (4-6 weeks)
Weeks 1-2: Conduct user interviews with 15-20 potential users from each target segment. Focus on understanding current solutions, pain points, and desired outcomes.
Weeks 3-4: Develop detailed user personas and journey maps. Identify critical moments where user satisfaction is most important.
Weeks 5-6: Create and test low-fidelity prototypes with target users. Validate core value propositions and user workflow assumptions.
This phase establishes the foundation for all subsequent development decisions and prevents costly changes later in the development process.
Phase 2: MVP Development with Core User Workflows (8-12 weeks)
Weeks 1-4: Build minimum viable product focusing on one primary user problem. Implement core features that directly address validated user needs. Starting with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) allows for quick launch and user feedback, enabling iterative improvements based on real user interactions.
Weeks 5-8: Develop basic user onboarding and core user workflows. Ensure that users can achieve their primary goal within the platform.
Weeks 9-12: Implement basic analytics and feedback collection systems. Test MVP with real users and gather systematic feedback.
The MVP should solve one problem exceptionally well rather than solving multiple problems adequately.
Phase 3: User Testing and Iteration Cycles (Ongoing 2-week sprints)
Implement continuous 2-week development cycles that include: * User testing of new features and improvements * Analysis of user behavior and platform analytics * Integration of user feedback into development priorities * Regular communication with users about platform changes. Iterating and evolving based on user needs and market changes is essential for the longevity of a digital platform, ensuring it remains relevant and effective.
- User testing of new features and improvements
- Analysis of user behavior and platform analytics
- Integration of user feedback into development priorities
- Regular communication with users about platform changes
Each sprint should deliver measurable improvements in user satisfaction or task completion rates.
Phase 4: Scaling Features Based on User Feedback
Expand platform capabilities based on validated user needs and behavior patterns. Prioritize features that serve the largest user segments while maintaining platform focus and usability.
Monitor user adoption of new features and iterate based on actual usage patterns rather than assumed user needs.
Phase 5: Advanced Personalization and Optimization
Implement machine learning and advanced personalization features that improve user experiences based on individual behavior and preferences.
Advanced optimization should enhance core functionality rather than adding complexity for its own sake.
Tools and Technologies for User-First Development
Selecting the right tools can accelerate user-first development while ensuring that technology choices support rather than constrain user experience goals.
No-Code Platforms for Rapid User-Focused Prototyping
LoftOS: Enables rapid creation of functional prototypes that can be tested with real users before committing to custom development.
Bubble: Provides sophisticated functionality for testing complex user workflows and interactions without extensive coding.
Webflow: Offers designer-friendly tools for creating high-fidelity prototypes that closely match intended user experiences.
No-code platforms allow rapid iteration and testing of user experience concepts before investing in custom development.
User Research Tools for Behavior Analysis
Hotjar: Provides heatmaps and session recordings that reveal how users actually interact with your platform rather than how they say they interact.
FullStory: Offers comprehensive user session capture that helps identify friction points and optimization opportunities.
UserTesting: Facilitates remote user testing sessions with target audiences, providing qualitative insights into user experience and satisfaction.
Design and Prototyping Tools
Figma: Enables collaborative design processes that keep user needs central to interface and interaction design decisions.
Sketch: Provides design tools specifically optimized for digital platform interface creation and iteration.
Adobe XD: Offers prototyping capabilities that allow testing of user interactions before development begins.
Analytics Platforms for User Insights
Google Analytics 4: Provides event-based tracking that reveals user paths, conversion patterns, and behavioral insights.
Mixpanel: Focuses on user actions and behaviors rather than page-based metrics, providing deeper insights into user engagement.
Amplitude: Offers advanced cohort analysis and user journey visualization that supports data-driven user experience decisions.
Customer Feedback Tools for Direct Communication
Intercom: Provides real-time communication channels that allow users to provide feedback and receive support without leaving your platform.
Zendesk: Offers comprehensive customer support tools that track user satisfaction and identify common user issues.
UserVoice: Facilitates user feedback collection and feature request management that keeps user needs central to development priorities.
A/B Testing Platforms for Experience Optimization
Optimizely: Provides robust testing frameworks that allow systematic optimization of user experiences based on actual user behavior.
VWO: Offers user-friendly testing tools that make it easy to test user experience improvements without extensive technical expertise.
Google Optimize: Integrates with other Google tools to provide accessible testing capabilities for user experience optimization.
Right tools selection should prioritize user research and feedback capabilities over impressive technical features that don’t serve user understanding or experience improvement.
Conclusion
Building user first digital platforms requires fundamentally shifting from technology-driven to user-driven development approaches. The most successful platforms prioritize understanding user needs, solving real problems, and delivering consistent value over showcasing technical capabilities or adding impressive features. Engaging with users and building a community around a digital platform can provide valuable insights and promote growth, creating a feedback loop that benefits both users and the platform.
This user-first approach delivers measurable business benefits: higher user engagement, better retention rates, lower customer acquisition costs, and stronger competitive advantage. Organizations that invest in thorough user research, iterative development, and continuous user feedback integration build platforms that users genuinely recommend and actively use.
The key to successful platform development lies in maintaining focus on user value throughout every decision—from initial strategy through technical architecture to ongoing feature development. When users succeed with your platform, your business succeeds as well.
Start your user-first platform journey today by conducting your first user interviews. Understanding your users deeply is the foundation for every subsequent success in building platforms that truly serve human needs while delivering business results.
